This go library was created / tested with
- go 1.18
- helheim 1.0.2 py310
go get -u github.com/bogdanfinn/helheim-go
// or specific version:
// go get -u github.com/bogdanfinn/helheim-go@v0.2.2It is not possible to use Bifrost with this library. This is due to the fact, that it is not possible to load a go library via CFFI into a go application. You end up with two go runtimes colliding. Bifrost is (partly?) written in go. If you want to use a TLS Client you have to implement your own TLS Client and pass the cookies from the helheim session to your client or use this https://github.com/bogdanfinn/tls-client.
char *helheimVersion(); is not in the default cffi lib you build out of the examples. Please check helheim discord
server how to add this function and then be able to call Version() on the helheimClient. The helheim client
with Version() moved to the branch with-version-func. Please use this instead of master when you modified the cffi
lib.
As Venom explained in the discord server you have make adjustments on the template file when building the shared library.
Next to the 'body': response.text, add 'content': base64.b64encode(response.content).decode('utf-8'). Do not forget to import base64. After building the shared library you should have Content filled on RequestResponseResponse type.
Please search in the discord server for the exact explanation.
See example in example_http_base64_body. You need to set the helheim_go.WithBase64Response() option on the http client.
Attention Venom dropped support for python 3.8 since some time. I upgraded directly to Python 3.10. It should be straight forward for you to follow this guide but do everything with python 3.10 instead of python 3.8
Install Python in a version which is compatible with helheim. I used this: https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.10.9/python-3.10.9-macos11.pkg
Important
Please make sure you installed python on mac from python.org. Had a couple of messages with some python errors during runtime which all were resolved after installing python from python.org instead of other sources.
On Windows I used https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.10.9/python-3.10.9-amd64.exe and makre sure to add Python to PATH during installation. You can get the Python Installation path by opening the CMD and type in python and hit enter. Then you execute the following code:
import sys
print(sys.path)
For me the output contained: C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38
Install Python in a version which is compatible with helheim. I used this:
apt-get update
apt-get upgrade
apt-get install python3 python3-dev python3-pip
python3 -m pip install -U --force-reinstall pip
Build the cffi library. It is very important that you download from discord the tar.gz file with the correct version
and for your system you are building your go app. In my case with the above installed python version on MacOS it
is helheim-0.8.7-py38-darwin.x86_64.tar.gz
On Ubuntu (amd64) it is helheim-0.8.7-py38-linux.x86_64.tar.gz. On Windows (amd64) it
is helheim-0.8.7-py38-windows.x86_64.tar.gz.
Install helheim by running python setup.py install in the projects root directory. This will install all the required dependencies for helheim.
After installation of dependencies you are able to install helheim / make updates by just running pip install -U helheim-0.8.7-py38-darwin.x86_64.tar.gz (with the correct package name)
Now build the cffi library as described in python example 3. Navigate inside the directory and run:
python build-cffi.py. In my case python3 build-cffi.py
On Windows I had to install some visual studio build tools.
This will create the following files for you:
helheim_cffi.chelheim_cffi.o-
helheim_cffi.dylib(MacOS) -
helheim_cffi.so(Linux) -
helheim_cffi.dll(Windows)
Copy the helheim_cffi library (dylib, so or dll) into your pythons lib directory. In my case it
is: /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/lib. Under Ubuntu it is: /usr/include/python3.10
Under Windows it is: C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38
Note: On Linux and MacOS create a duplicate of the cffi library file and name it libhelheim_cffi.dylib (MacOS)
or libhelheim_cffi.so (Linux). I have to keep both files in the directory to get the example running.
In addition copy the helheim_cffi.dylib file in your working directory of your running app or use the following env
variable to start your application:
# Specify where application finds the cffi lib file on runtime
# MacOS
# DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH="/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/lib" ./yourCompiledAppBinary
# Linux
# LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/usr/include/python3.10" ./yourCompiledAppBinary
# Windows
# just copy the .dll next to your built .exe file.
#
# We assume here that you copied the cffi lib file into the applications working directory and we do not need to define the path to the library
# ./yourCompiledAppBinary
Due to the fact that we are loading a C dynamic library we need to build our app with cgo. That is done by adding a few
flags and env vars to our go build command. Check ./example/build.sh for the correct go build command. This script
will build the example application located in ./example/main.go
You have to adjust the different paths according to your setup/system in build.sh
If you run your go project inside the Goland IDE check out the branch local-debug which contains the build flags in the
code to be parsed from the IDE when you work with IDE Run Configurations.
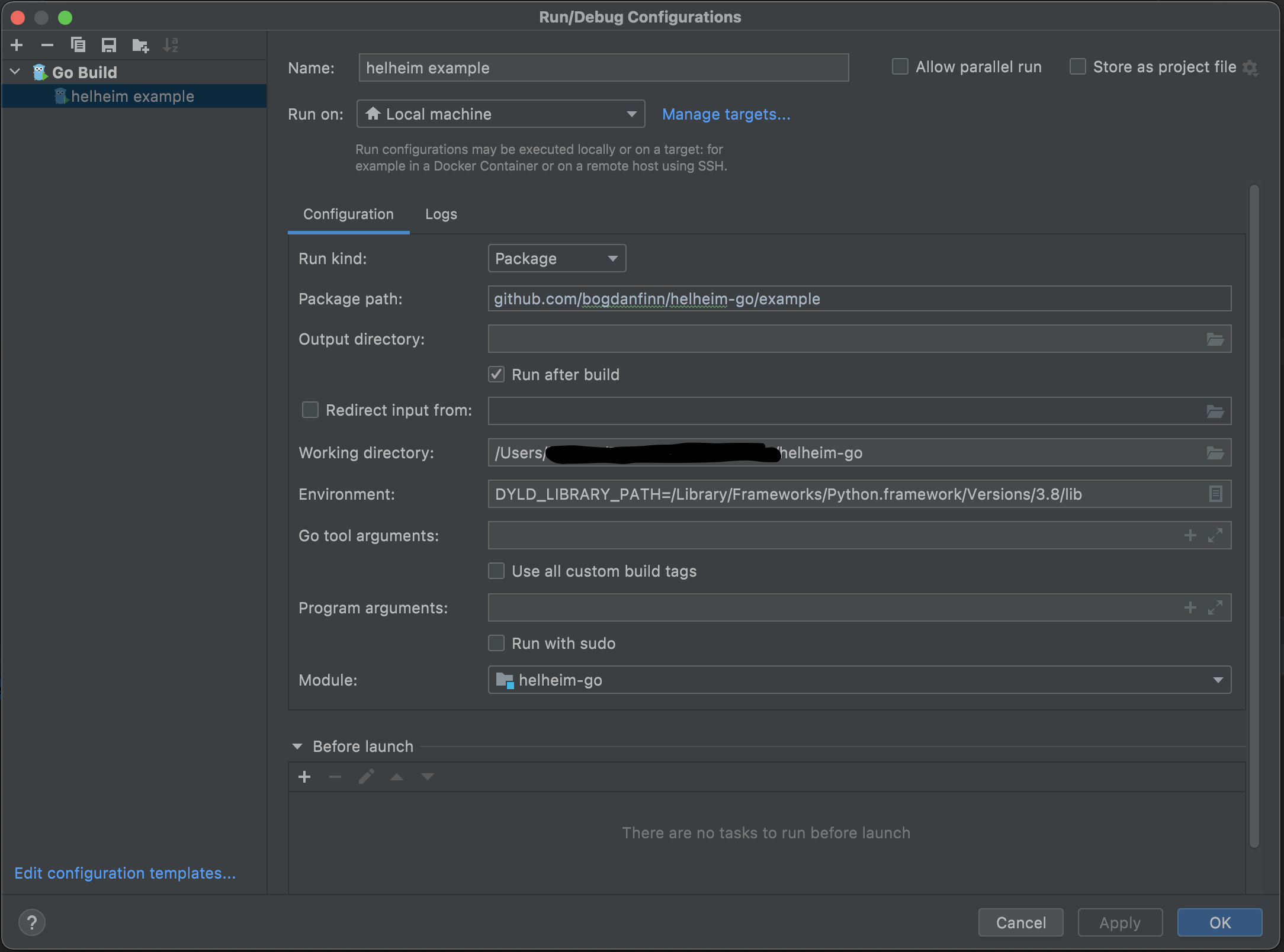 Always be aware of the arguments you have to provide for your system based on the fact where your helheim cffi lib is located as explained in
Always be aware of the arguments you have to provide for your system based on the fact where your helheim cffi lib is located as explained in build.sh
In .vscode is a launch configuration for vscode with the paths of build.sh.
Currently I can't get the example app successfully running with a debugger. It starts and i can set breakpoints (before the first helheim function call) and everything works fine. When i first call a helheim function while debugging the application the debugger and the app are silently crashing.
package main
import (
helheim_go "github.com/bogdanfinn/helheim-go"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// NewClient() returns each time a new instance which is requesting helheims auth() endpoint
// helheimClient, err := helheim_go.NewClient("YOUR_API_KEY", false, false, nil)
// Provide() is creating one helheim client instance and returning the same authenticated instance on every Provide() call
// withAutoReAuth can be set to false actually because the helheim lib itself has re-auth logic in place.
helheimClient, err := helheim_go.ProvideClient("YOUR_API_KEY", false, false, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
log.Println("helheim client initiated")
// check possible options in the python examples
options := helheim_go.CreateSessionOptions{
Browser: helheim_go.BrowserOptions{
Browser: "chrome",
Mobile: false,
Platform: "windows",
},
Captcha: helheim_go.CaptchaOptions{
Provider: "vanaheim",
},
}
session, err := helheimClient.NewSession(options)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
log.Println("session initiated")
reqOpts := helheim_go.RequestOptions{
Method: http.MethodGet,
Url: "https://www.genx.co.nz/iuam/",
Options: make(map[string]string),
}
resp, err := session.Request(reqOpts)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
log.Println("response:")
log.Println(resp)
}For more examples check ./example/main.go
After creating your helheim client you are able to call helheimClient.NewHttpClient(options, helheimClientOptions...) on it to receive an instance
of a struct which implements an interface which is more or less compatible with golangs net/http client.
With this solution you do not have to alter the code where you use a golang net/http Client in order to implement helheim logic. Your basic code could look similar to this (error handling removed):
req, _ := http.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, "https://www.genx.co.nz/iuam/", nil)
resp, _ := httpCLient.Do(req)In order to use helheim with a minimum amount of effort you can create a httpClient like this:
package main
import (
helheim_go "github.com/bogdanfinn/helheim-go"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// NewClient() returns each time a new instance which is requesting helheims auth() endpoint
// helheimClient, err := helheim_go.NewClient("YOUR_API_KEY", false, false, nil)
// Provide() is creating one helheim client instance and returning the same authenticated instance on every Provide() call
// withAutoReAuth can be set to false actually because the helheim lib itself has re-auth logic in place.
helheimClient, err := helheim_go.ProvideClient("YOUR_API_KEY", false, false, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
log.Println("helheim client initiated")
options := helheim_go.CreateSessionOptions{
Browser: helheim_go.BrowserOptions{
Browser: "chrome",
Mobile: false,
Platform: "windows",
},
Captcha: helheim_go.CaptchaOptions{
Provider: "vanaheim",
},
}
helheimClientOptions := []helheim_go.HttpClientOption{
helheim_go.WithWokou("chrome"),
// add here other options like proxy or debug
// helheim_go.WithDebug(),
// helheim_go.WithProxyUrl("http://username:password@host:port"),
}
httpCLient, err := helheimClient.NewHttpClient(options, helheimClientOptions...)
// this httpClient can then be used like a net/http Client
}For the full http client example check ./example_http/main.go