Spring boot + MyBatis codebase containing real world examples (CRUD, auth, advanced patterns, etc) that adheres to the RealWorld spec and API.
This codebase was created to demonstrate a fully fledged full-stack application built with Spring boot + Mybatis including CRUD operations, authentication, routing, pagination, and more.
For more information on how to this works with other frontends/backends, head over to the RealWorld repo.
Following some DDD principles. REST or GraphQL is just a kind of adapter. And the domain layer will be consistent all the time. So this repository implement GraphQL and REST at the same time.
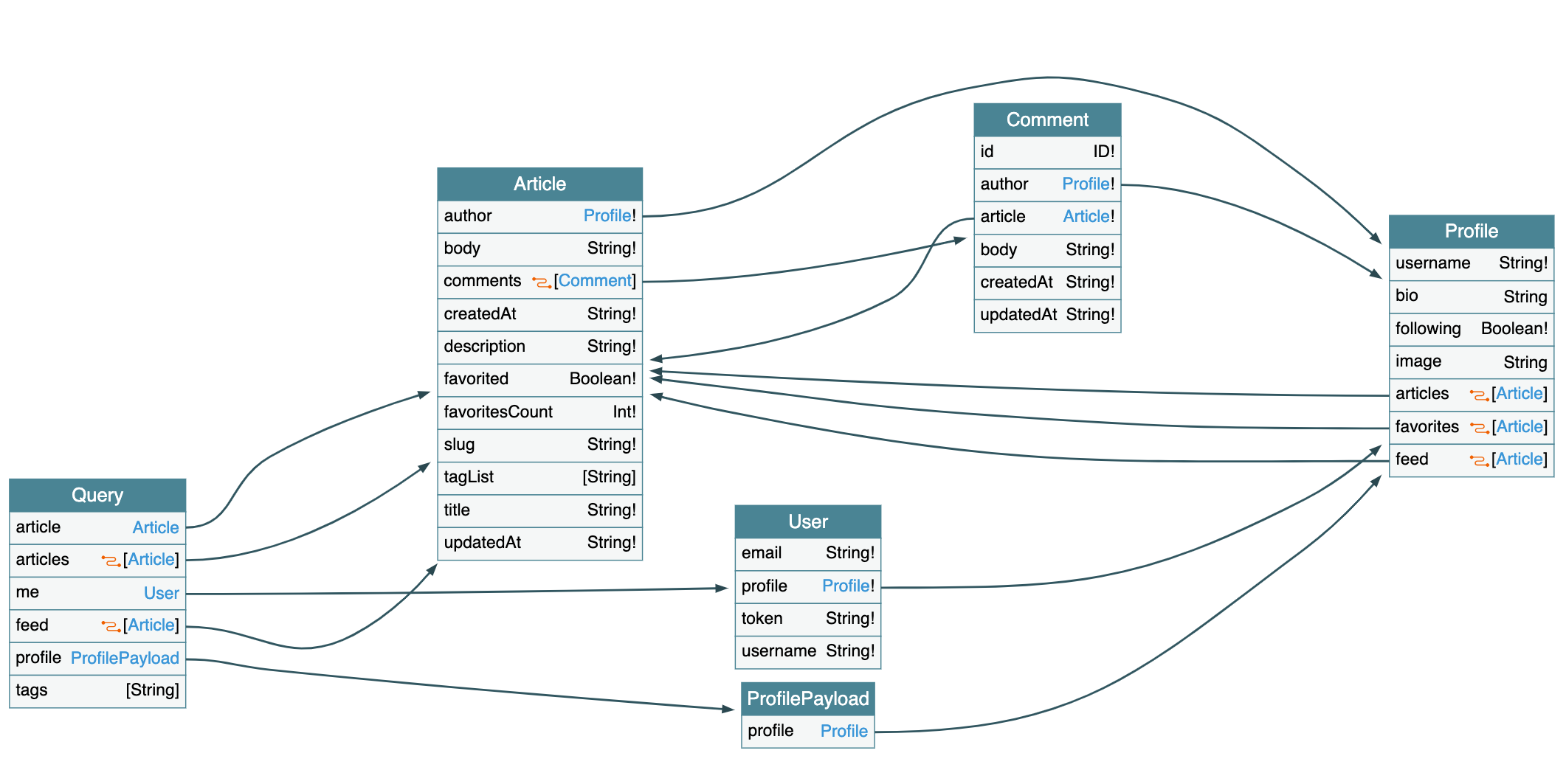
The GraphQL schema is https://github.com/gothinkster/spring-boot-realworld-example-app/blob/master/src/main/resources/schema/schema.graphqls and the visualization looks like below.
And this implementation is using dgs-framework which is a quite new java graphql server framework.
The application uses Spring Boot (Web, Mybatis).
- Use the idea of Domain Driven Design to separate the business term and infrastructure term.
- Use MyBatis to implement the Data Mapper pattern for persistence.
- Use CQRS pattern to separate the read model and write model.
And the code is organized as this:
-
apiis the web layer implemented by Spring MVC -
coreis the business model including entities and services -
applicationis the high-level services for querying the data transfer objects -
infrastructurecontains all the implementation classes as the technique details
Integration with Spring Security and add other filter for jwt token process.
The secret key is stored in application.properties.
It uses a H2 in-memory database sqlite database (for easy local test without losing test data after every restart), can be changed easily in the application.properties for any other database.
You'll need Java 11 installed.
./gradlew bootRun
To test that it works, open a browser tab at http://localhost:8080/tags .
Alternatively, you can run
curl http://localhost:8080/tags
Try it out with Docker
You'll need Docker installed.
./gradlew bootBuildImage --imageName spring-boot-realworld-example-app
docker run -p 8081:8080 spring-boot-realworld-example-app
The entry point address of the backend API is at http://localhost:8080, not http://localhost:8080/api as some of the frontend documentation suggests.
The repository contains a lot of test cases to cover both api test and repository test.
./gradlew test
Use spotless for code format.
./gradlew spotlessJavaApply
Please fork and PR to improve the project.