An easy-to-use testing module, that doesn't require the terminal!
pip install error404
Or download the project here
For the first parameter of the test function, insert the function and its input
Then, add the expected result:
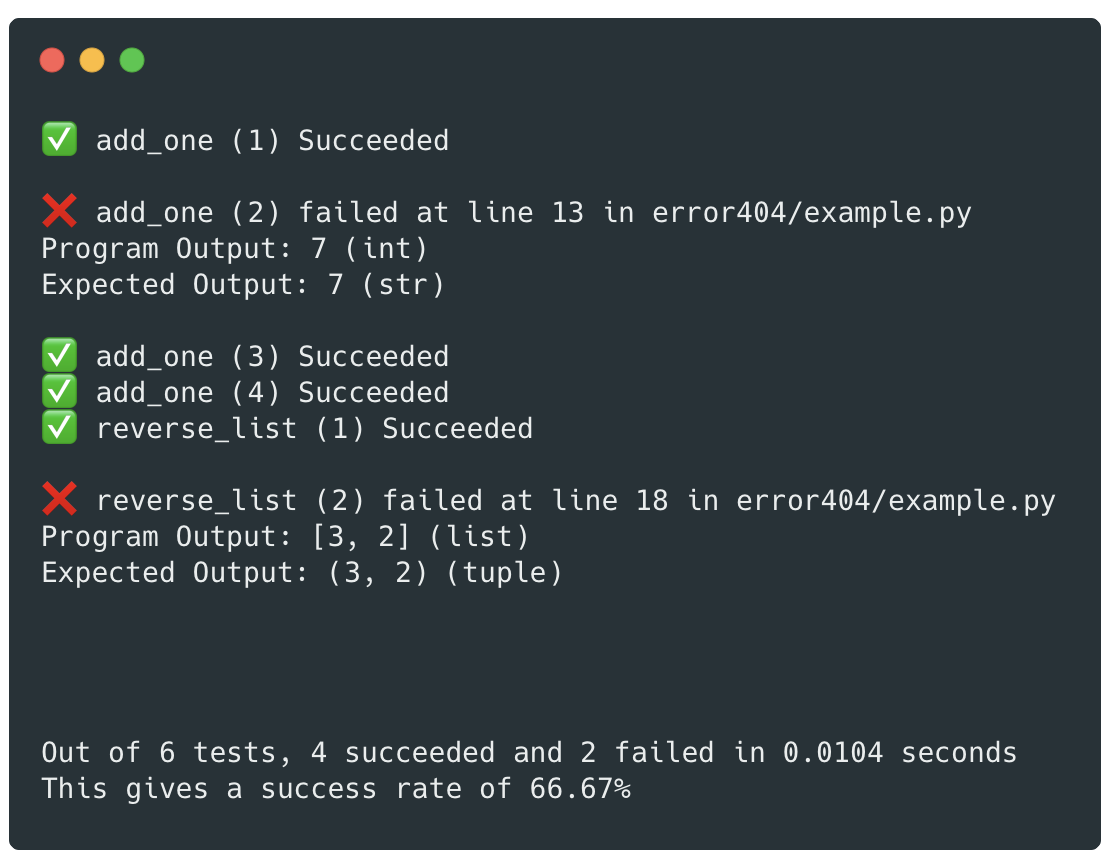
test(some_function(function_input), expected_result)This example produces the output shown above 👆
Only the test function has to be imported
test_results is run at the end to display how many succeeded
from error404 import test
# Example Functions
def add_one(number):
return number + 1
def reverse_list(user_list):
return user_list[::-1]
# Test Cases
test(add_one(4), 5) # Passes
test(add_one(6), "7") # Fails: Different type
test(add_one(232), 233) # Passes
test(add_one(-2), -1) # Passes
test(reverse_list([1, 2, 3]), [3, 2, 1]) # Passes
test(reverse_list([2, 3]), (3, 2)) # Fails: Different typeIn interactive mode, you can still use just the test function
However, if you want to restart the counter, import clear_results, which is silent.
If you want to see the overall results, import test_results. This also runs clear_results afterwards.
from error404 import test, test_results
>>> def demo(greeting):
return greeting
>>> test(demo('hi'), 'hi')
✅ Function (1) Succeeded
>>> test(demo('bye'), 'hello')
❌ Function (2) failed at line 1 in Interactive Mode
Program Output: bye (str)
Expected Output: hello (str)
>>> test_results()
Out of 2 tests, 1 succeeded and 1 failed in 0.4561 seconds
This gives a success rate of 50.0%
This works similar to a normal file. However, make sure to run test_results or clear_results (silent) at the end of the cell. Otherwise, the counter will continue in the following cells.
This project is licensed under the GNU General Public License v3.0