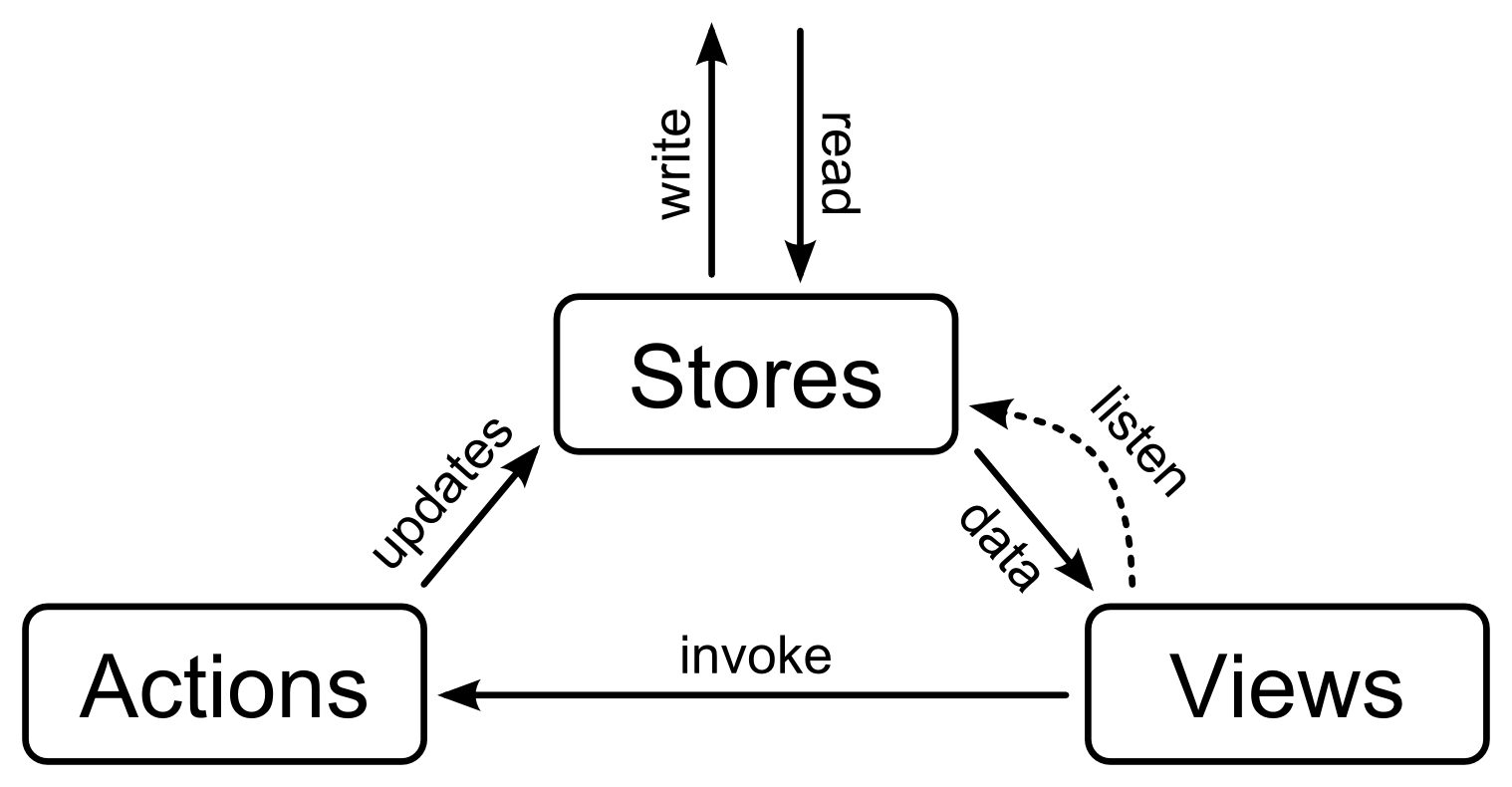
A simple flux-like architecture with a syncing items store.
A store that manages read and write access to items (accessed by a string id).
It
- offers synchronous access to items
- caches items after reading
- fires update events for items
- merges multiple writes to items
- let writes do optimistic updates
A helper which repeatedly calls a function until all references items are available. The ItemsStoreFetcher can fetch from multiple stores.
A helper class which leases multiple items from multiple stores. It captures dependencies from calling a function.
A wrapper for a React component. It expects a static getProps method from the component that calculate props from stores (and params when using react-router). The wrapper container handles listening to changes and charging of stores.
The usable API inside the getProps method is very simple and synchronous. See API > createContainer.
The container exposes a static chargeStores method to charge the stores.
The constructor.
desc A description of the store. The creator provides options and read/write methods that the store will use.
initialData An object containing initial item data. You may pass the result of getData here. This should be used for initializing the stores after server-side rendering.
The store description. The behavior of the store changes depending on the contained keys. Can contain these keys:
reading and writing
readSingleItem: function(item, callback) Reads a single item. item is an object { id: string, oldData: any|undefined }. callback is a function(err, newData: any|undefined).
readMultipleItems: function(items, callback) Reads multiple items. Similar to readSingleItem but items is an array and the callback is a function(err, newDatas: object) where newDatas is an object containing items id as key (prefixed with any single char) and value is the new data. i. e. {"_12345": { name: "item 12345" }}.
writeSingleItem: function(item, callback) Writes a single item. item is an object { id: string, update: any, oldData: any|undefined, newData: any }. callback is a function(err).
writeMultipleItems: function(items, callback) Writes multiple items. Similar to writeSingleItem but items is an array.
createSingleItem: function(item, callback) Creates a single item. item is an object { data: any }. callback is a function(err, newId).
createMultipleItems: function(items, callback) Creates multiple items. Similar to createSingleItem but items is an array.
deleteSingleItem: function(item, callback) Deletes a single item. item is an object { id: string }. callback is a function(err).
deleteMultipleItems: function(items, callback) Deletes multiple items. Similar to deleteSingleItem but items is an array.
writeAndReadSingleItem: function(item, callback) A combination of writeSingleItem followed by a readSingleItem.
writeAndReadMultipleItems: function(items, callback) A combination of writeMultipleItems followed by a readMultipleItems.
createAndReadSingleItem: function(items, callback) A combination of createSingleItem followed by a readSingleItem. callback is function(err, newId, newData).
createAndReadMultipleItems: function(items, callback) A combination of createMultipleItems followed by a readMultipleItems. callback is function(err, newIds: array, newDatas: object).
maxCreateItems Maximum of items allowed to be created by createMultipleItems or createAndReadMultipleItems.
maxWriteItems Maximum of items allowed to be written by writeMultipleItems or writeAndReadMultipleItems.
maxDeleteItems Maximum of items allowed to be delete by deleteMultipleItems.
maxReadItems Maximum of items allowed to be read by readMultipleItems.
You need to provide at least one read method. If you want to do updates you need to provide at least one write or writeAndRead method.
Reading or writing multiple items is preferred if more than one items should be read or written.
writeAndRead methods are preferred over write methods.
If multiple requests are scheduled they are processed in this order: 1. create, 2. write, 3. delete, 3. read.
updates
applyUpdate: function(data, update) Apply an update to existing data. The new data is returned. Doesn't modify data.
applyUpdate defaults to an method that merges (flat) the keys from update into data.
mergeUpdates: function(a, b) Merges two update. A new update is returned that represents applying update a and b.
mergeUpdates default to an flat merge.
rebaseUpdate: function(update, oldData, newData) Called when new data is received while an item was already changed locally. Returns a new update that behaves to newData like update to oldData.
rebaseUpdate default to an identity function that just returns update.
applyNewData: function(oldData, newData) Apply new data (from ItemsStore.setItemData) to old data. The new data for the item is returned. Usually the function doesn't modify oldData, but this is not required by items-store (but react requires immutable props and state). A possible optimization is to return the oldData object when it is equal to newData (and do the same for nested objects).
applyNewData defaults to an identity function that just returns newData.
applyNewError: function(oldData, newError) Same as applyNewData, but for ItemsStore.setItemError. The new data for the item is returned. Usually the function returns same kind of marker data that signals an error to readers. The function should not modify oldData, but it can copy it to the error marker to display cached data in cause of an error.
applyNewError defaults to a function that returns null.
timing
queueRequest: function(fn) Called when the store want to do something. It's called with a async function fn(callback) that should be called sometime in the future. You should wait at least one tick before calling fn if you want multiple reads/writes to be merged. You can use a shared queue to queue from multiple stores.
Defaults to process.nextTick.
Returns the current data of the item id. Returns undefined if no data is available. May return outdated cached data.
Returns status information about the item id. Returns an object with these keys:
available Any data is available.
outdated The item is outdated and a read is queued or will be queue when the item is read.
updated The item was changed and a write is queued.
listening Somebody is interested in this item.
Returns true if any data is available.
Returns true if data is available and not outdated.
Listen to changes of the item id. handler is called with the new data. A lease is returned which has a single method close which stops listening.
When calling listenToItem twice with the same id and handler no new lease is created. Instead the old lease is returned.
Calling this method may trigger a read to the item.
Waits until the item id is up to date and calls the callback once it's up to date.
Calling this method may trigger a read to the item.
Returns an object containing the data for every available item.
Applies the update to item id. The format of update depends on the provided applyUpdate implementation.
Calling this method trigger a write to the item.
Triggers a server request to create a new item. callback is called with the server response.
Triggers a server request to delete an item. callback is called with the server response.
Defines all available items as outdated.
Defines item id as outdated.
Defines all available items as outdated and
-
all = false(default): triggers reads for items which are listened. -
all = true: triggers reads for all items
Defines item id as outdated and triggers a read.
Sets the current item data newData for the item id. Should only be called when receiving data from a higher instance i. e. from the server or database.
You can use it in provided read and write methods when getting more information that the requested one. You should use this method when receiving data from an open stream.
Calls fn (function(addDependency)) multiple times until all referenced items are available. Than calls callback (function(err, result)) with the return value.
If fn throws an error callback is called immediately with the error.
The provided function addDependency(Store, id) tell the fetcher that the fn used Store to read an item id. You must call it for each item read. You must not write to stores.
Create a new instance.
Calls fn (function(addDependency)) and starts listening to item updates (if not already listening). onUpdate is called when an item was updated. Calling this method also stops listening to items that are no longer referenced by the fn.
The provided function addDependency(Store, id) tell the fetcher that the fn used Store to read an item id. You must call it for each item read. You must not write to stores.
Stops listening to item updates.
Creates a wrapper react component which handles store access and data listening.
It uses update batching of react, so you must ensure that all calls to ItemsStore.setItemData and callbacks of read... are inside the react event system, batched with ReactUpdates.batchedUpdates or use a continuous batching strategy (i. e. ReactRAFBatchingStrategy).
component
It's expected from the component to provide a static getProps function.
The context of the component must contain a key stores which is an object containing all stores (i. e. {Messages: [ItemsStore], Users: [ItemsStore]}).
This function should create the component props from stores and params and return it.
stores is an object containing a dependency-tracking version of each store i. e.
{
Messages: {
getItem: [Function],
getItemInfo: [Function],
isItemAvailable: [Function],
isItemUpToDate: [Function]
},
Users: {
getItem: [Function],
getItemInfo: [Function],
isItemAvailable: [Function],
isItemUpToDate: [Function]
}
}
params is the params object from react-router (if used)
Example for a getProps method:
statics: {
getProps: function(stores, params) {
if(!stores.Threads.isItemAvailable(params.threadId))
return { loading: true };
var thread = stores.Threads.getItem(params.threadId);
return {
thread: thread,
messages: thread.messages.map(function(messageId) {
var message = stores.Messages.getItem(messageId);
return message && Object.assign({}, message, {
user: stores.Users.getItem(message.userId)
});
})
}
}
}wrapper methods
Prepares stores with an ItemsStoreFetcher.
stores The object of ItemsStores, like the stores key in the context.
params params object from react-router.
Helpers to create actions:
{ [Function trigger]
listen: [Function listen]
}An action can be triggered by calling it. Any number of arguments can be provided.
An action has a listen (function(callback, bindContext)) method to listen to the action.
var singleAction = Actions.create();
singleAction(); // trigger
singleAction(1, 2, "hello"); // trigger with actions
singleAction.listen(function(a, b, c) {
console.log(a, b, c);
}, this);
var actions = Actions.create([
"someAction",
"otherAction"
]);
actions.someAction();
actions.otherAction("other");Creates a single action (without names parameter) or multiple actions (with names (string[]) parameter).
https://github.com/webpack/react-starter
-
readAndStreamSingleItem,readAndStreamMultipleItems - Timeout for cached data
- Maximum size of cached data