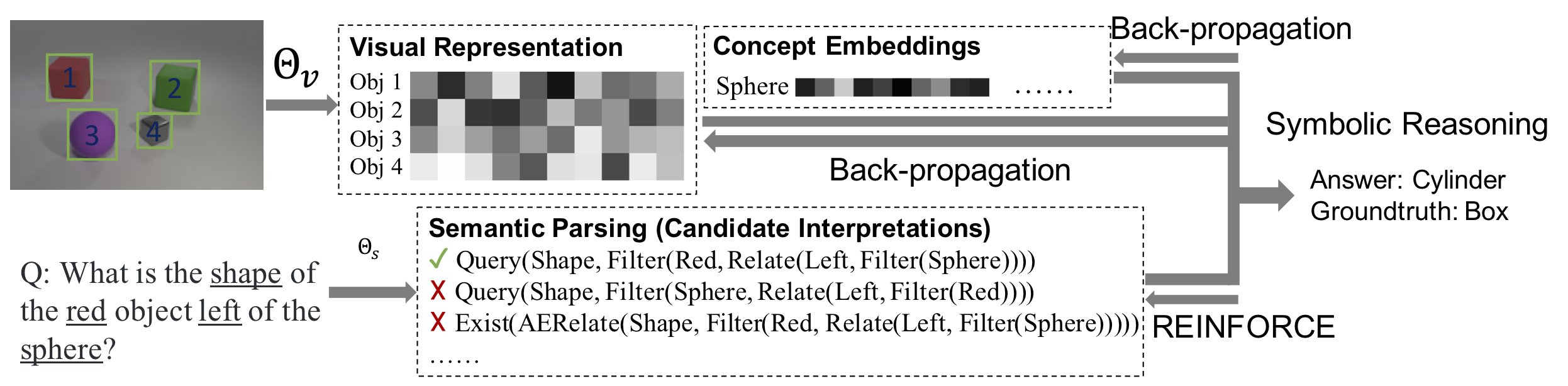
Pytorch implementation for the Neuro-Symbolic Concept Learner (NS-CL).
The Neuro-Symbolic Concept Learner: Interpreting Scenes, Words, and Sentences From Natural Supervision
Jiayuan Mao,
Chuang Gan,
Pushmeet Kohli,
Joshua B. Tenenbaum, and
Jiajun Wu
In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2019 (Oral Presentation)
[Paper]
[Project Page]
[BibTex]
@inproceedings{Mao2019NeuroSymbolic,
title={{The Neuro-Symbolic Concept Learner: Interpreting Scenes, Words, and Sentences From Natural Supervision}},
author={Mao, Jiayuan and Gan, Chuang and Kohli, Pushmeet and Tenenbaum, Joshua B and Wu, Jiajun},
booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2019},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJgMlhRctm}
}
- Python 3
- PyTorch 1.0 or higher, with NVIDIA CUDA Support
- Other required python packages specified by
requirements.txt. See the Installation.
Install Jacinle: Clone the package, and add the bin path to your global PATH environment variable:
git clone https://github.com/vacancy/Jacinle --recursive
export PATH=<path_to_jacinle>/bin:$PATH
Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/vacancy/NSCL-PyTorch-Release --recursive
Create a conda environment for NS-CL, and install the requirements. This includes the required python packages
from both Jacinle NS-CL. Most of the required packages have been included in the built-in anaconda package:
conda create -n nscl anaconda
conda install pytorch torchvision -c pytorch
To replicate the experiments, you need to prepare your dataset as the following. Taking the CLEVR dataset as an example.
clevr
├── train
│ ├── images
│ ├── questions.json
│ ├── scenes-raw.json
│ └── scenes.json
│ └── vocab.json
└── val
├── images
├── questions.json
├── scenes-raw.json
└── scenes.json
└── vocab.json
You can download all images, and put them under the images/ folders from the official website of the CLEVR dataset.
The questions.json and scenes-raw.json could also been found on the website.
Next, you need to add object detection results for scenes. Here, we use the tools provided by ns-vqa. In short, a pre-trained Mask-RCNN is used to detect all objects. We provide the json files with detected object bounding boxes at clevr/train/scenes.json and clevr/val/scenes.json.
The vocab.json could be downloaded at this URL.
Note: This current release contains only training codes for the visual modules. That is, currently we still assume that a semantic parser is pre-trained using program annotations. In the full NS-CL, this pre-training is not required. We also plan to release the full training code soon.
To train the model:
jac-crun <gpu_id> scripts/trainval.py --desc experiments/clevr/desc_nscl_derender.py --training-target derender --curriculum all --dataset clevr --data-dir <data_dir>/clevr/train --batch-size 32 --epoch 100 --validation-interval 5 --save-interval 5 --data-split 0.95
The --data-split 0.95 specifies that five percent of the training data will be held out as the develop set. Since the annotation for the test split is not available for the CLEVR dataset, we will test our model on the original validation split.
A sample training log is provided at this URL. A pretrained model is available at this URL.
To test on the validation split, you need to download the clevr/val/questions.json that includes parsed programs at this URL. Note that since we do not include any annotated programs during training, the parsed programs in this file can be different from the original CLEVR dataset (due to the "equivalence" between programs).
jac-crun <gpu_id> scripts/trainval.py --desc experiments/clevr/desc_nscl_derender.py --training-target derender --curriculum all --dataset clevr --data-dir <data_dir>/clevr/train --data-split 0.95 --extra-data-dir data/clevr/val --evaluate --load dumps/clevr/desc_nscl_derender/derender-curriculum_all-qtrans_off/checkpoints/epoch_100.pth
Here, we input the CLEVR validation split as an --extra-data-dir, so the performance on the CLEVR validation split will be shown as the accuracy on the extra dataset split.
Example output (validation/acc/qa denotes the performance on the held-out dev set, while validation_extra/acc/qa denotes the performance on the official validation split):
validation/acc/qa = 0.994886
validation/acc/qa/count = 0.989113
validation/acc/qa/count_equal = 0.993470
validation/acc/qa/count_greater = 0.999275
validation/acc/qa/count_less = 0.998321
validation/acc/qa/exist = 0.996974
validation/acc/qa/query = 0.997189
validation/acc/qa/query_attribute_equal = 0.995861
# performance on CLEVR's validation set.
validation_extra/acc/qa = 0.996146
validation_extra/acc/qa/count = 0.992547
validation_extra/acc/qa/count_equal = 0.993377
validation_extra/acc/qa/count_greater = 0.996390
validation_extra/acc/qa/count_less = 0.998373
validation_extra/acc/qa/exist = 0.997652
validation_extra/acc/qa/query = 0.997664
validation_extra/acc/qa/query_attribute_equal = 0.996723